Swelling of the salivary glands, also known as sialadenitis, is a common medical condition affecting the mouth and throat. It occurs when one or more salivary glands become inflamed due to various causes, including infection, trauma, obstruction, or autoimmune disease. These conditions can result in a range of symptoms, making it essential to recognize the signs and seek appropriate medical attention.
One of the hallmark symptoms of salivary gland inflammation is facial swelling, typically concentrated near the area where saliva drains from the mouth. This swelling can be accompanied by localized pain. Individuals experiencing sialadenitis may also notice dryness in the mouth, making it uncomfortable to speak or swallow food and liquids. Additional salivary gland tumor symptoms can include fever, chills, and persistent bad breath.
The leading cause of sialadenitis is a bacterial infection, commonly involving bacteria such as streptococcus or staphylococcus. These pathogens can enter the salivary gland through openings in the skin near the gland or via direct contact with contaminated saliva. Infections trigger an inflammatory response, resulting in the characteristic swelling and discomfort. Viruses, fungi, and certain medications, particularly antibiotics when not taken correctly, can also irritate the salivary glands and contribute to the development of sialadenitis.
Diagnosing sialadenitis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. They may assess for signs of infection, such as redness and tenderness around the affected area. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Pain in the Area of the Glands: Causes and Considerations
Pain in the area of the glands can be indicative of various medical conditions, necessitating a thorough evaluation to pinpoint the underlying cause. Glands throughout the body play crucial roles in hormone production, fluid secretion, and toxin filtration. When pain occurs in these regions, it can signify an underlying health issue that warrants attention.
Inflammation and infection are common culprits behind gland-related pain. Inflammatory responses can arise from autoimmune reactions, injuries, or infections. Conditions like Lyme disease, HIV, and mononucleosis may lead to swelling, redness, tenderness, and pain upon touch in the affected gland area. Less frequent causes of glandular pain include tumours, cysts, or abscesses, which may require surgical intervention if they exert significant pressure or discomfort on nearby structures.
Neurological issues can also manifest as gland-related pain. Conditions such as trigeminal neuralgia, characterized by irritated nerve fibres causing sharp, shooting facial pains, or carpal tunnel syndrome, involving compressed nerves leading to tingling sensations and numbness, can affect the glandular regions. Additionally, systemic conditions like fibromyalgia, costochondritis (inflammation in the chest wall), and chronic fatigue syndrome, which may involve painful lymph nodes, can contribute to discomfort in various areas, including the glands.
Difficulty Opening the Mouth or Jaw: Causes and Assessment
Difficulty opening the mouth or jaw is a common issue with numerous potential causes. Understanding these underlying factors is essential for appropriate management and treatment.
One of the primary causes of difficulty opening the mouth or jaw is temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder. This condition arises when the joints connecting the lower jaw to the skull become inflamed, leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility. TMJ disorder can result from factors like teeth clenching or grinding, stress, arthritis, facial or jaw trauma, misalignment due to accidents or birth defects, genetic predisposition, and more.
Another possible cause of mouth or jaw restriction is trismus, commonly referred to as “lockjaw.” Trismus occurs due to inflammation in the muscles responsible for chewing (masticatory muscles). This condition can stem from various factors, including dental abscesses, radiation therapy targeting head and neck cancers, and inflammation related to habits like bruxism.
Numbness or Tingling Sensation in the Face, Neck, and Head
Experiencing numbness or tingling sensations in the face, neck, or head area can be concerning, as these symptoms may indicate various underlying conditions. Understanding potential causes is crucial for proper evaluation and management.
Several common factors can lead to numbness or tingling sensations in these regions. Tension headaches pinched nerves in the neck or cervical spine, migraines, and trigeminal neuralgia (a nerve disorder affecting one side of the face) are among the potential culprits. Conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome (nerve entrapment in the wrist), stroke-related symptoms such as hemiplegia (paralysis on one side), multiple sclerosis (an autoimmune-related nerve damage disorder), and transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes) can also manifest as numbness or tingling. Furthermore, certain medications, including some antidepressants, may provoke these sensations.
If numbness or tingling persists for an extended period without relief, it is imperative to seek prompt medical advice. Healthcare providers will inquire about accompanying symptoms and conduct appropriate evaluations to ascertain the underlying cause.
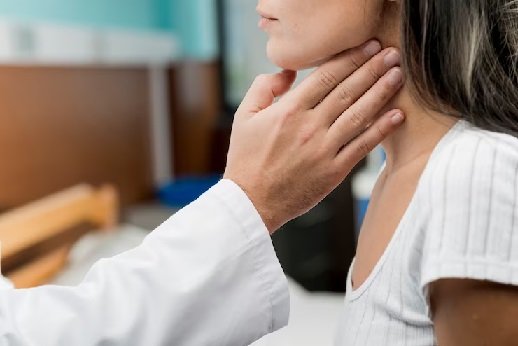
Change in Voice Quality or Difficulty Speaking
Experiencing difficulty speaking or changes in voice quality can be distressing and impact one’s quality of life. This article explores the potential causes and available treatments for voice-related issues, shedding light on common conditions and their management.
Laryngitis is one of the leading causes of voice changes and difficulty speaking. It involves inflammation of the larynx (voice box) and can result from various factors, including viral or bacterial infections, injuries, allergies, acid reflux, or exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke or air pollution. Symptoms of laryngitis may include hoarseness, a sore throat, pain when speaking, and challenges in projecting one’s voice. Typically, rest and avoidance of vocal strain are recommended treatments, although antibiotics may be necessary if symptoms persist beyond two weeks.
Neurological conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease, can also lead to changes in voice quality or difficulty speaking. These issues may arise from involuntary movements affecting speech production. Individuals experiencing voice-related problems should consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Unusual Taste in Mouth: Causes and Considerations
Experiencing an unusual taste in the mouth can be disconcerting, and it’s essential to understand the potential causes and when to seek medical guidance for persistent symptoms.
One common cause of an odd taste in the mouth is dehydration. Inadequate fluid intake can decrease saliva production, resulting in a dry mouth and metallic or sour taste sensations. Other potential causes include medication or supplement side effects, sinus or throat infections, poor oral hygiene leading to bacterial growth on the tongue or teeth, smoking, regular alcohol consumption, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause, digestive issues like acid reflux (GERD), and specific cancer treatments, such as radiation therapy with chemotherapy.
When faced with an unusual taste that lingers, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider. Doctors may perform tests, including blood work, to identify the root cause. Treatment recommendations will vary based on the underlying condition.
Bleeding from the Salivary Gland Area: Understanding Causes
Experiencing bleeding from the salivary gland area can be alarming. While it may result from minor issues, it can also signal a more serious medical condition. It is crucial to comprehend the potential causes of this symptom to seek appropriate care.
Salivary glands are located in various regions of the mouth and throat, including near the jaw and behind the ears. The most common type
of salivary glands, the parotid glands is situated on either side of the face, beneath the cheeks. Saliva production serves essential functions in digestion, immune protection, and maintaining mouth moisture during activities like speaking and eating.
The primary cause of bleeding from the salivary gland area is often trauma or injury to the gland itself or the surrounding structures, such as teeth, gums, tongue, or lips. Such trauma can occur due to accidental biting or chewing on hard food, aggressive brushing with a toothbrush that has hard bristles, or other similar incidents. Infections, like mumps virus infections, can also lead to swelling and inflammation within the affected gland(s), potentially causing bleeding.
Sensitivity to Cold Temperatures: Causes and Considerations
For individuals sensitive to cold temperatures, even slight drops in temperature can lead to discomfort or pain. This article delves into the potential causes of cold sensitivity and explores possible treatments for managing this condition.
Cold sensitivity can result from a combination of factors, including genetics, medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and environmental elements. Genetics play a crucial role in determining how the body responds to temperature variations. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or Raynaud’s disease, can increase sensitivity to cold temperatures. Lifestyle factors like smoking or inadequate clothing during cold weather can also impact an individual’s ability to tolerate low temperatures. Furthermore, residing in colder climates or prolonged exposure to winter conditions can contribute to heightened cold sensitivity.
People with cold sensitivity often experience uncomfortable symptoms when exposed to lower temperatures, such as chills, numbness, tingling sensations on the skin surface, and joint aches throughout the body. While these symptoms are typically benign, individuals experiencing severe discomfort should consult their healthcare provider for guidance and potential interventions.
Lump on Inside Cheek or Side of Neck: Causes and Concerns
Discovering a lump on the inside cheek or the side of the neck can raise concerns. Understanding the potential causes and when to seek medical evaluation is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Lumps in these areas can arise from various conditions, ranging from minor irritations to potentially serious medical issues. Most lumps are benign and may be attributed to factors like swollen lymph nodes, cysts, inflamed salivary glands, or even an abscessed tooth. However, more severe causes, such as oral cancer or thyroid nodules, should not be ruled out.
If a lump is accompanied by fever, pain, or swelling, immediate medical attention is warranted. Additionally, if a lump persists for more than two weeks or undergoes changes in size or shape, it should be examined by a healthcare professional. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and may include laboratory tests, such as blood work and imaging scans like X-rays or CT scans, depending on the suspected cause.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms and potential causes of various oral and throat-related issues is essential for prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention. Seeking timely medical advice when experiencing these symptoms can lead to effective treatment and improved overall well-being.
